BSS ServiceAgent Design Clarifications¶
Purpose¶
This document clarifies the design patterns, component boundaries, and implementation contexts for the BSS serviceAgent function and its helper functions as they relate to the BSS Rider Workflow and DIRAC framework integration.
Source Traceability¶
- Parent Document:
bss-rider-workflow.md - Implementation:
bss-agent-v2.ts - Architecture Context: DIRAC framework component boundaries
1. ServiceAgent Design Pattern Overview¶
Core Architecture Principle¶
The serviceAgent function operates as a delegation hub that:
1. Receives external inputs from various DIRAC components via MQTT/API
2. Routes requests to specific helper functions based on action type
3. Maintains uniform interface across all helper functions
4. Coordinates state management through centralized AgentStateManager
5. Returns standardized results for FSM integration and external systems
Single Function Interface Pattern¶
// External Interface (Public)
const serviceAgent: CalculationFunction = async (request: ExternalRequest, context: CalculationContext): Promise<AgentResult>
// Helper Functions (Private)
type AgentHelperFunction = (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState) => Promise<PartialOutcome>
Key Design Decision: All helper functions use identical signatures to enable consistent routing, testing, and maintenance.
2. DIRAC Component Boundary Clarifications¶
2.1 ABS Platform Responsibilities (This Agent)¶
Core Service Coordination¶
- ✅ Service plan state management (agent_state, service_account validation)
- ✅ Business logic validation (quotas, access rights, bundle requirements)
- ✅ FSM state transitions (service_cycle, payment_cycle coordination)
- ✅ MQTT signal emission (intent signals, allocation instructions)
- ✅ Cross-service state updates (battery assignments, quota consumption)
W1: Asset Dependency Resolution¶
/**
* CONTEXT: UXI mobile app requests asset information for rider
* CONTRACT: Return fleet IDs only - ARM resolves to specific assets
* BOUNDARY: ABS provides fleet dependencies, ARM handles asset queries
*/
const getRequiredAssetIds = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Analyze service bundle → identify required fleet types
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Map service requirements → fleet categories
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Validate location context against service plan
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Return fleet IDs with dependency mapping
// ARM DELEGATION: Fleet ID → specific asset resolution
// ARM DELEGATION: Location-based asset filtering
// ARM DELEGATION: Asset availability and pagination
}
W2: Service Intent Signal Emission¶
/**
* CONTEXT: Customer announces intent to receive service at location
* CONTRACT: Emit MQTT signal with customer and service context
* BOUNDARY: ABS emits signal, external location personnel/systems respond
*/
const emitServiceIntentSignal = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Validate customer eligibility and location compatibility
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Compose service requirements from bundle
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Emit structured MQTT signal
// EXTERNAL DELEGATION: Location personnel notification
// EXTERNAL DELEGATION: Location system preparation
}
W3: Customer-Location Binding¶
/**
* CONTEXT: Customer physically arrives and authenticates at location
* CONTRACT: Establish secure service session and validate access
* BOUNDARY: ABS handles service validation, location systems handle physical access
*/
const bindCustomerToLocation = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Service account validation
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Access rights verification
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Session establishment and security
// LOCATION DELEGATION: Physical access control (door locks, bay access)
// LOCATION DELEGATION: Personnel notification
// UXI DELEGATION: Session token management for mobile app
}
W4: Fleet Allocation Signal¶
/**
* CONTEXT: Instruct fleet assets to perform specific service sequence
* CONTRACT: Send fleet-level instruction, ARM resolves to specific assets
* BOUNDARY: ABS instructs fleet, ARM coordinates individual assets
*/
const sendAssetAllocationSignal = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Fleet instruction composition
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Service context and requirements
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: MQTT signal emission with echo expectation
// ARM DELEGATION: Fleet → specific asset resolution
// ARM DELEGATION: Asset allocation and coordination
// ASSET DELEGATION: Physical service execution
}
W5: Service State Updates & Billing¶
/**
* CONTEXT: Service completed, update all related states and handle billing
* CONTRACT: Coordinate multi-asset state updates and quota management
* BOUNDARY: ABS handles state coordination, Odoo processes payments
*/
const updateServiceStatesAndBilling = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Battery asset assignment updates
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Service metrics and quota consumption
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Invoice generation for quota overages
// ABS RESPONSIBILITY: Cross-service state synchronization
// ODOO DELEGATION: Payment processing and collection
// BIA DELEGATION: Analytics and reporting
// ARM DELEGATION: Asset state persistence
}
2.2 ARM (Asset Relations Management) Responsibilities¶
What ARM Handles¶
- ✅ Fleet → Asset Resolution: Convert fleet IDs to specific available assets
- ✅ Location-based Filtering: Apply geographic constraints to asset queries
- ✅ Asset Availability Queries: Real-time asset status and availability
- ✅ Asset Allocation Coordination: Manage specific asset assignments
- ✅ IoT Asset Communication: Direct communication with physical assets
- ✅ Asset State Persistence: Maintain current_asset assignments
ARM Integration Pattern¶
// ABS emits fleet-level signals
const fleetInstruction = {
fleet_id: 'fleet-swap-stations-nairobi',
service_requirements: { /* ABS context */ },
arm_resolution_required: {
resolve_to_specific_assets: true,
location_filtering: 'apply_location_filter',
asset_selection_criteria: 'availability_and_proximity'
}
};
// ARM resolves and coordinates specific assets
// ARM responds with echo containing specific asset details
const armResponse = {
fleet_id: 'fleet-swap-stations-nairobi',
resolved_asset_id: 'cabinet_001',
service_completion_details: { /* actual service results */ }
};
2.3 UXI (Unified User Experience) Responsibilities¶
What UXI Handles¶
- ✅ Asset Display: Present asset data from ARM in map/list formats
- ✅ User Interaction: QR code scanning, location selection, service requests
- ✅ Session Management: Handle authentication tokens and session state
- ✅ Real-time Updates: Display service progress and status updates
- ✅ Cross-platform Experience: Web and mobile app consistency
UXI Integration Pattern¶
// UXI requests asset information
const uxiRequest = {
action: 'GET_REQUIRED_ASSET_IDS',
rider_location: { lat: -1.2921, lng: 36.8219 },
search_radius: 10
};
// ABS returns fleet IDs, ARM provides asset details to UXI
const uxiAssetData = {
assets: [ /* ARM-provided asset details */ ],
display_format: 'map_with_pagination',
interaction_capabilities: ['qr_scan', 'manual_selection']
};
2.4 Odoo (ERP Platform) Responsibilities¶
What Odoo Handles¶
- ✅ Payment Processing: Credit card transactions, mobile money, bank transfers
- ✅ Invoice Management: Generate, send, and track invoices
- ✅ Subscription Management: Recurring billing and plan renewals
- ✅ Customer Relationship Management: Customer data and communication
- ✅ Financial Reporting: Revenue tracking and financial analytics
Odoo Integration Pattern¶
// ABS generates invoices for quota overages
const invoiceData = {
service_id: 'svc-battery-fleet-kenya-premium',
overage_amount: 2, // 2 swaps over quota
billing_rate: 10, // $10 per swap
total_charge: 20
};
// Odoo processes payment and syncs back to ABS
const odooSync = {
action: 'SYNC_ODOO_SUBSCRIPTION',
odoo_subscription_id: 12345,
odoo_payment_state: 'paid',
odoo_subscription_state: 'in_progress'
};
3. External Input Sources and Routing¶
3.1 MQTT Listener Integration¶
The serviceAgent receives inputs from multiple sources through the MQTT listener and plugin registry:
/**
* MQTT Topic Patterns for BSS Agent
*/
const MQTT_SUBSCRIPTIONS = [
// Direct service requests
'request/BSS/+/+', // request/BSS/{customer_id}/{action}
// Echo responses from external systems
'echo/BSS/fleet_allocation/+/completed', // Asset service completion
'echo/BSS/location_action/+/completed', // Location action completion
// Odoo synchronization
'sync/BSS/odoo/subscription/+', // Odoo subscription updates
'sync/BSS/odoo/payment/+', // Odoo payment status updates
// UXI user interactions
'interaction/BSS/asset_request/+', // Asset discovery requests
'interaction/BSS/service_intent/+', // Service intent declarations
'interaction/BSS/location_binding/+', // Customer location binding
];
3.2 Request Type Mapping¶
/**
* External Input → Helper Function Mapping
* Each input type routes to specific helper function
*/
const REQUEST_TYPE_MAPPING = {
// UXI Mobile App Requests
'GET_REQUIRED_ASSET_IDS': getRequiredAssetIds,
'EMIT_SERVICE_INTENT_SIGNAL': emitServiceIntentSignal,
'BIND_CUSTOMER_TO_LOCATION': bindCustomerToLocation,
// ARM Integration Requests
'SEND_ASSET_ALLOCATION_SIGNAL': sendAssetAllocationSignal,
'UPDATE_SERVICE_STATES_AND_BILLING': updateServiceStatesAndBilling,
// Odoo Integration Requests
'SYNC_ODOO_SUBSCRIPTION': syncOdooSubscription,
// Core Service Operations
'CHECK_PAYMENT': checkPaymentStatus,
'CHECK_SERVICE': checkServiceAvailability,
'ALLOCATE_ASSET': processAssetAllocation
};
3.3 Context Expectations for Helper Functions¶
Request Data Context (External Input)¶
interface RequestData {
// UXI Context
rider_location?: { lat: number; lng: number };
search_radius?: number;
auth_token?: string;
// Location Context
location_id?: string;
target_location_id?: string;
session_token?: string;
// Service Context
service_sequence?: string;
requested_services?: string[];
// Asset Context
target_fleet_id?: string;
service_completion_details?: {
old_battery_id: string;
new_battery_id: string;
energy_transferred: number;
service_duration: number;
};
// Odoo Context
odoo_subscription_id?: number;
odoo_payment_state?: string;
odoo_subscription_state?: string;
}
Plan State Context (Internal State)¶
interface PlanState {
// Core Service Plan Data
id: string;
customer_id: string;
service_account: string;
service_bundle: string;
// Usage and Quota State
quota_used: number;
quota_limit: number;
swaps_today: number;
total_energy_consumed: number;
// Payment and Subscription State
payment_status: string;
subscription_start: string;
subscription_end: string;
// Agent-specific State (managed by AgentStateManager)
agent_state: {
agent_version: string;
swaps_today: number;
suspended_until: string | null;
execution_count: number;
// Odoo Integration Fields
odoo_subscription_id?: number;
odoo_last_sync_at?: string;
odoo_payment_state?: string;
odoo_subscription_state?: string;
};
}
4. Implementation Context and Contracts¶
4.1 Helper Function Implementation Pattern¶
/**
* STANDARD HELPER FUNCTION TEMPLATE
* All helper functions follow this exact pattern
*/
const helperFunctionTemplate = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// 1. CONTEXT VALIDATION
// Validate required input parameters from external systems
// Check component boundary responsibilities
// 2. BUSINESS LOGIC EXECUTION
// Apply validation rules using Validator Array Pattern
// Execute core business logic within ABS domain
// 3. EXTERNAL SYSTEM COORDINATION
// Emit MQTT signals for external component actions
// Prepare data for component delegation
// 4. STATE MANAGEMENT
// Update agent state using centralized AgentStateManager
// Prepare FSM inputs for state transitions
// 5. STANDARDIZED RESPONSE
return {
signals: ['PRIMARY_SIGNAL', 'SECONDARY_SIGNAL'],
metadata: {
called: 'helperFunctionName',
reason: 'Clear explanation of outcome',
// Detailed context for debugging and integration
component_delegations: {
arm: 'What ARM should do with this result',
uxi: 'What UXI should do with this result',
odoo: 'What Odoo should do with this result'
},
// External system coordination
mqtt_signals: {
emitted: [/* signals sent */],
expected_echoes: [/* expected responses */]
}
},
fsmInputs: [
{ cycle: 'service_cycle', input: 'FSM_INPUT_NAME' }
]
};
};
4.2 Component Delegation Contracts¶
ARM Delegation Contract¶
// When ABS delegates to ARM
interface ARMDelegation {
fleet_ids: string[]; // Fleet IDs to resolve
location_context?: string; // Location filtering context
asset_selection_criteria: string; // Selection algorithm hint
expected_response: {
asset_details: boolean; // Return specific asset data
availability_status: boolean; // Include availability info
location_mapping: boolean; // Include location coordinates
};
}
UXI Delegation Contract¶
// When ABS provides data for UXI
interface UXIDelegation {
display_data: any; // Data for user interface
interaction_capabilities: string[]; // Available user actions
session_management: {
session_token?: string; // Secure session identifier
expiration?: string; // Session timeout
permissions: string[]; // Allowed operations
};
}
Odoo Delegation Contract¶
// When ABS delegates to Odoo
interface OdooDelegation {
invoice_generation: {
service_id: string;
overage_amount: number;
billing_rate: number;
};
subscription_sync: {
abs_service_plan_id: string;
expected_odoo_response: string[];
};
}
4.3 Error Handling and Recovery Patterns¶
/**
* STANDARDIZED ERROR HANDLING
* Consistent error response across all helper functions
*/
const handleComponentError = (errorType: string, context: any): PartialOutcome => {
return {
signals: [`${errorType}_ERROR`],
metadata: {
error_type: errorType,
error_context: context,
recovery_actions: {
immediate: 'What can be done immediately',
retry_policy: 'How to retry the operation',
fallback_options: 'Alternative approaches'
},
component_impacts: {
arm: 'How ARM should handle this error',
uxi: 'How UXI should display this error',
odoo: 'How Odoo should handle this error'
}
}
};
};
5. Development Guidelines and Best Practices¶
5.1 Code Comments for Implementation Context¶
/**
* W1: Asset Dependency Resolution
*
* EXTERNAL INTEGRATION CONTEXT:
* - INPUT SOURCE: UXI mobile app (rider requesting asset information)
* - OUTPUT TARGET: ARM microservice (for asset resolution)
* - BOUNDARY: ABS provides fleet IDs, ARM resolves to specific assets
*
* IMPLEMENTATION PATH:
* 1. Analyze rider's service bundle → identify required fleet types
* 2. Map service requirements → fleet categories (swap stations, batteries)
* 3. Apply location context if provided
* 4. Return fleet IDs with dependency mapping for ARM resolution
*
* COMPONENT DELEGATION:
* - ARM: Resolves fleet IDs to specific available assets
* - UXI: Displays asset data in map/list format with pagination
* - External: No external system involvement at this stage
*/
const getRequiredAssetIds = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// CONTEXT: UXI rider needs to see available assets for service
// CONTRACT: Return fleet IDs only - ARM handles asset resolution
const riderLocation = requestData.rider_location;
const serviceBundle = planState.bundle_services || ['battery_swap'];
// IMPLEMENTATION LOGIC...
};
/**
* W2: Service Intent Signal Emission
*
* EXTERNAL INTEGRATION CONTEXT:
* - INPUT SOURCE: UXI mobile app (customer declaring service intent)
* - OUTPUT TARGET: Location personnel/systems via MQTT
* - BOUNDARY: ABS emits signal, location systems respond
*
* IMPLEMENTATION PATH:
* 1. Validate customer eligibility for target location
* 2. Extract service requirements from customer's bundle
* 3. Compose comprehensive intent signal payload
* 4. Emit MQTT signal with proper topic structure
*
* COMPONENT DELEGATION:
* - Location Systems: Receive notification and prepare for customer
* - Personnel: Get notified of incoming customer and service needs
* - External: Physical location preparation and notification
*/
const emitServiceIntentSignal = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// CONTEXT: Customer announces intent to receive service
// CONTRACT: Emit structured MQTT signal for location coordination
const customerId = planState.customer_id;
const targetLocationId = requestData.target_location_id;
// IMPLEMENTATION LOGIC...
};
5.2 Testing Strategy for Helper Functions¶
/**
* UNIT TEST PATTERN FOR HELPER FUNCTIONS
* Each helper function should have comprehensive test coverage
*/
describe('BSS Agent Helper Functions', () => {
describe('W1: getRequiredAssetIds', () => {
it('should return fleet IDs for basic battery swap service', async () => {
const requestData = {
rider_location: { lat: -1.2921, lng: 36.8219 },
search_radius: 10
};
const planState = {
bundle_services: ['battery_swap'],
customer_tier: 'standard'
};
const result = await getRequiredAssetIds(requestData, planState);
expect(result.signals).toContain('SERVICE_ACTIVATED'); // External signal compressed to FSM
expect(result.metadata.fleet_ids).toHaveProperty('swap_station_fleet');
expect(result.metadata.arm_resolution_context).toBeDefined();
});
it('should handle location validation errors', async () => {
const requestData = {
location_id: 'INVALID_STATION'
};
const planState = {
bundle_services: ['battery_swap']
};
const result = await getRequiredAssetIds(requestData, planState);
expect(result.signals).toContain('LOCATION_NOT_ALLOWED');
});
});
describe('Component Integration Tests', () => {
it('should properly delegate to ARM for asset resolution', async () => {
// Test ARM integration contract
});
it('should emit proper MQTT signals for external systems', async () => {
// Test MQTT signal structure and delivery
});
});
});
5.3 Documentation Standards¶
/**
* DOCUMENTATION TEMPLATE FOR NEW HELPER FUNCTIONS
*
* @function {functionName}
* @description Brief description of what this function does
*
* @context
* - External Input Source: Where this request originates
* - Target Recipients: Which systems will use the output
* - DIRAC Boundary: What this component handles vs delegates
*
* @contract
* - Input Requirements: What data must be provided
* - Output Guarantees: What the function promises to return
* - Side Effects: What external actions are triggered
*
* @delegation
* - ARM: What ARM should do with the results
* - UXI: How UXI should handle the response
* - Odoo: Any Odoo integration requirements
* - External: Any external system coordination
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const result = await functionName(
* { input: 'data' },
* { plan: 'state' }
* );
* ```
*/
6. Integration Patterns and Signal Flow¶
6.1 Complete Signal Flow Example¶
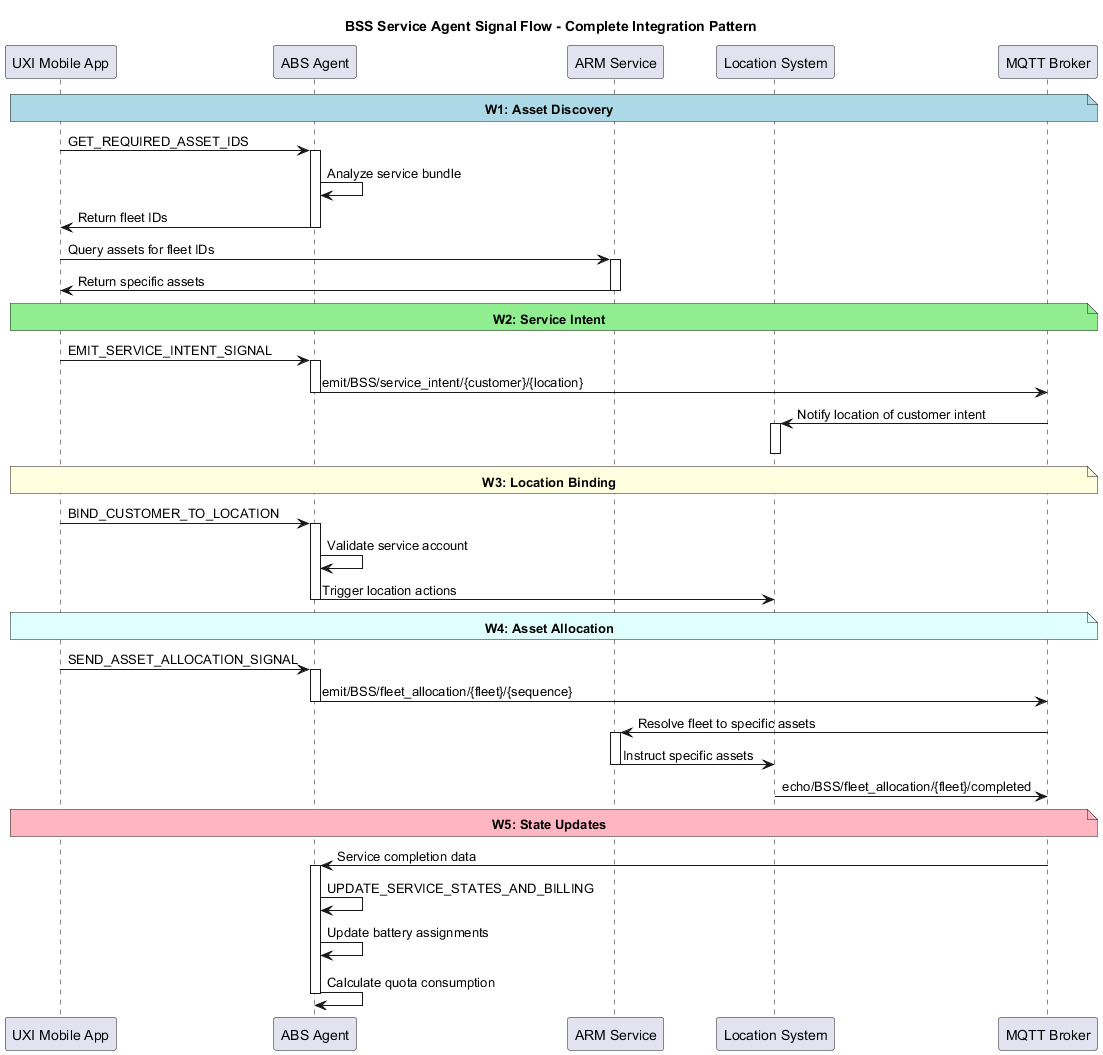
Figure: Complete BSS Service Agent Signal Flow showing integration between UXI, ABS Agent, ARM Service, Location System, and MQTT Broker across five key workflows (W1-W5).
6.2 Error Recovery Patterns¶
/**
* ERROR RECOVERY STRATEGY FOR EACH WORKFLOW
*/
const ERROR_RECOVERY_PATTERNS = {
'W1_ASSET_DISCOVERY_FAILED': {
immediate_action: 'Return cached fleet IDs if available',
retry_strategy: 'Exponential backoff with ARM service',
fallback_option: 'Default to nearest known assets',
user_notification: 'Limited asset selection available'
},
'W2_INTENT_SIGNAL_FAILED': {
immediate_action: 'Queue signal for retry',
retry_strategy: 'Immediate retry up to 3 attempts',
fallback_option: 'Direct UXI notification to user',
user_notification: 'Please contact location directly'
},
'W3_BINDING_REJECTED': {
immediate_action: 'Return specific rejection reason',
retry_strategy: 'No automatic retry - user action required',
fallback_option: 'Suggest alternative locations',
user_notification: 'Service not available at this location'
},
'W4_ALLOCATION_TIMEOUT': {
immediate_action: 'Log timeout and check echo queue',
retry_strategy: 'Single retry with extended timeout',
fallback_option: 'Manual allocation through location personnel',
user_notification: 'Service request sent to location'
},
'W5_STATE_UPDATE_FAILED': {
immediate_action: 'Queue state updates for background processing',
retry_strategy: 'Persistent retry until success',
fallback_option: 'Manual reconciliation required',
user_notification: 'Service completed - processing transaction'
}
};
7. Performance and Scalability Considerations¶
7.1 O(1) Agent Operation Requirements¶
/**
* PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR HELPER FUNCTIONS
* All helper functions must maintain O(1) or O(log n) performance
*/
const PERFORMANCE_GUIDELINES = {
'getRequiredAssetIds': {
max_execution_time: '50ms',
complexity: 'O(1) - fleet mapping is constant time',
caching_strategy: 'Cache fleet mappings by service bundle type'
},
'emitServiceIntentSignal': {
max_execution_time: '100ms',
complexity: 'O(1) - direct MQTT emission',
caching_strategy: 'No caching needed - real-time signal'
},
'bindCustomerToLocation': {
max_execution_time: '200ms',
complexity: 'O(1) - direct validation checks',
caching_strategy: 'Cache location capabilities and restrictions'
},
'sendAssetAllocationSignal': {
max_execution_time: '100ms',
complexity: 'O(1) - fleet instruction composition',
caching_strategy: 'No caching - real-time coordination'
},
'updateServiceStatesAndBilling': {
max_execution_time: '300ms',
complexity: 'O(n) where n = number of affected services',
caching_strategy: 'Batch state updates when possible'
}
};
7.2 Scalability Patterns¶
/**
* SCALABILITY CONSIDERATIONS FOR HIGH-VOLUME DEPLOYMENT
*/
const SCALABILITY_PATTERNS = {
'horizontal_scaling': {
pattern: 'Stateless helper functions enable horizontal scaling',
requirement: 'Agent state must be externally managed',
implementation: 'AgentStateManager handles state persistence'
},
'async_processing': {
pattern: 'Non-critical operations use async processing',
requirement: 'State updates can be eventual consistency',
implementation: 'Queue non-critical updates for background processing'
},
'circuit_breaker': {
pattern: 'External system failures should not block core operations',
requirement: 'Graceful degradation when components unavailable',
implementation: 'Fallback responses when ARM/Odoo unavailable'
}
};
8. Future Extension Points¶
8.1 New Helper Function Template¶
/**
* TEMPLATE FOR ADDING NEW HELPER FUNCTIONS
* Follow this pattern for consistent implementation
*/
const newHelperFunction = async (requestData: RequestData, planState: PlanState): Promise<PartialOutcome> => {
// STEP 1: CONTEXT VALIDATION
// - Validate required input parameters
// - Check component boundary responsibilities
// - Ensure proper external integration context
// STEP 2: BUSINESS LOGIC EXECUTION
// - Apply Validator Array Pattern for consistency
// - Execute core business logic within ABS domain
// - Maintain O(1) or O(log n) performance
// STEP 3: EXTERNAL SYSTEM COORDINATION
// - Emit MQTT signals for external component actions
// - Prepare delegation data for other DIRAC components
// - Handle component boundary contracts
// STEP 4: STATE MANAGEMENT
// - Update agent state using AgentStateManager
// - Prepare FSM inputs for state transitions
// - Ensure state consistency across services
// STEP 5: STANDARDIZED RESPONSE
return {
signals: ['PRIMARY_OUTCOME_SIGNAL'],
metadata: {
called: 'newHelperFunction',
reason: 'Clear explanation of what happened',
component_delegations: {
arm: 'What ARM should do',
uxi: 'What UXI should do',
odoo: 'What Odoo should do'
},
performance_metrics: {
execution_time_ms: 'actual execution time',
operations_performed: 'count of major operations'
}
},
fsmInputs: [
{ cycle: 'service_cycle', input: 'APPROPRIATE_FSM_INPUT' }
]
};
};
// STEP 6: REGISTER IN ACTION HANDLERS
const ActionHandlers: Record<string, AgentHelperFunction> = {
'NEW_ACTION_TYPE': newHelperFunction,
// ... existing handlers
};
8.2 Component Integration Extensions¶
/**
* EXTENSION POINTS FOR NEW DIRAC COMPONENT INTEGRATIONS
*/
interface ComponentIntegrationExtension {
component_name: string;
integration_pattern: 'mqtt_signals' | 'api_calls' | 'event_sourcing';
delegation_contract: {
input_format: any;
output_format: any;
error_handling: string;
};
helper_functions: string[]; // Which functions integrate with this component
}
const FUTURE_INTEGRATIONS: ComponentIntegrationExtension[] = [
{
component_name: 'BIA (Business Intelligence)',
integration_pattern: 'event_sourcing',
delegation_contract: {
input_format: 'ServiceMetrics[]',
output_format: 'AnalyticsResult',
error_handling: 'graceful_degradation'
},
helper_functions: ['updateServiceStatesAndBilling']
},
{
component_name: 'TEAMS (Communications)',
integration_pattern: 'mqtt_signals',
delegation_contract: {
input_format: 'NotificationRequest',
output_format: 'DeliveryConfirmation',
error_handling: 'retry_with_fallback'
},
helper_functions: ['emitServiceIntentSignal', 'bindCustomerToLocation']
}
];
9. Summary and Action Items¶
9.1 Key Design Clarifications¶
- Single Function Interface:
serviceAgentacts as a delegation hub with uniform helper function signatures - Component Boundaries: Clear separation between ABS coordination, ARM asset management, UXI user interface, and Odoo payment processing
- External Integration: MQTT-based signaling for component coordination with structured echo patterns
- State Management: Centralized AgentStateManager for consistent state handling across all helper functions
- Error Recovery: Standardized error patterns with component-specific recovery strategies
9.2 Implementation Guidelines¶
- Context Comments: Every helper function must include context, contract, and delegation comments
- Validator Array Pattern: Use consistent validation patterns for business logic
- Performance Requirements: Maintain O(1) or O(log n) performance for all operations
- Component Contracts: Clearly define what each DIRAC component should do with function outputs
- Testing Strategy: Comprehensive unit and integration tests for each helper function
9.3 Next Steps for Development¶
- Update Existing Functions: Add context comments to all current helper functions
- Component Integration Tests: Create tests for ARM, UXI, and Odoo integration patterns
- Error Recovery Implementation: Implement standardized error recovery for each workflow
- Performance Monitoring: Add execution time monitoring to helper functions
- Documentation Updates: Update technical documentation with component delegation contracts
This document provides the complete context and clarifications needed for implementing and maintaining the BSS serviceAgent and its helper functions within the DIRAC framework architecture.