BSS Service Consumption Workflow¶
Workflow Diagram¶
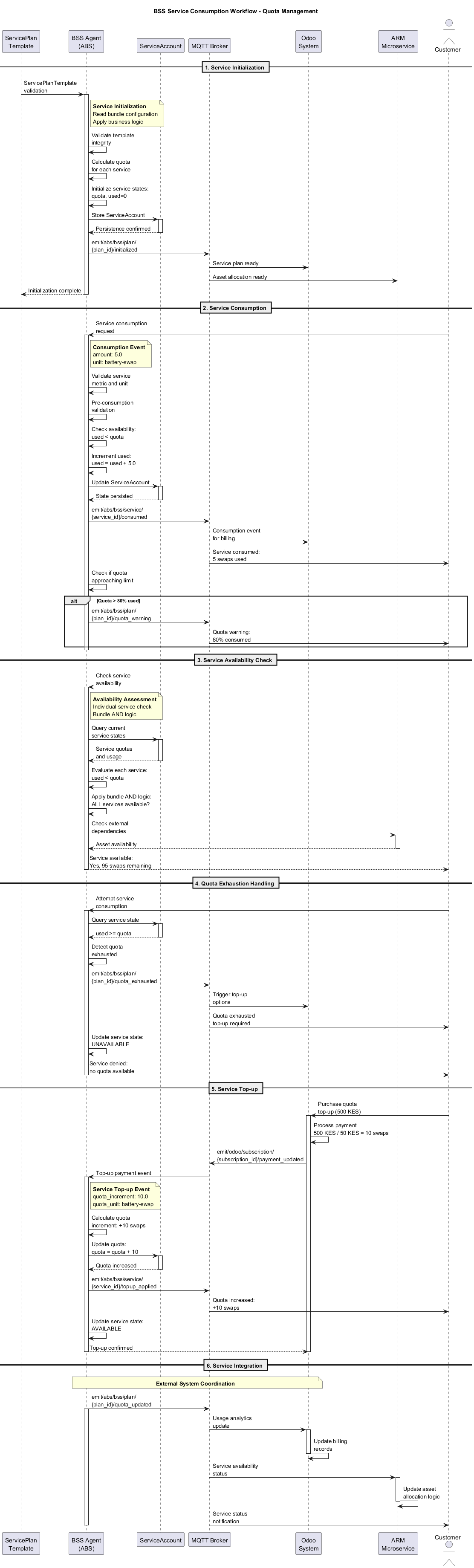
Complete sequence diagram showing the service consumption lifecycle: 1 (Service Initialization), 2 (Service Consumption), 3 (Service Availability Check), 4 (Quota Exhaustion Handling), 5 (Service Top-up), and 6 (Service Integration), with interactions between ServicePlan templates, BSS Agent, ServiceAccount, Odoo, ARM, and customers.
Overview¶
This document outlines the comprehensive service consumption workflow for the Battery Swap Service (BSS) system, focusing on four core areas:
- Service Initialization - Setting up appropriate quota levels based on service bundle business logic and template configurations
- Service Consumption - Tracking usage increments according to service bundle logic with comprehensive validation
- Service Availability - Determining availability based on quota vs usage comparison with real-time monitoring
- Service Integration - Coordinating with external systems (Odoo, ARM, UXI) using established MQTT patterns
Core Principles¶
Bundle AND Logic¶
- A service plan becomes unavailable if ANY single service in its bundle is exhausted
- All services in a bundle must be available for the bundle to be considered available
- This ensures coherent service delivery across all bundled components
- No Partial Service Rule: Service must not proceed if any validation fails or conditions are not fully met
Finite Resource Management¶
- Services as Finite Resources: Each service represents a finite, consumable resource with measurable limits
- Quota vs Used Tracking: Each service has individual
quota(initial allocation) andused(consumed amount) tracking - Availability Logic: Service is available when
used < quota; exhausted whenused >= quota - Progressive Consumption: As services are rendered,
usedincreases whilequotaremains constant until exhaustion - Service Metrics: All consumption must be expressed in the underlying service metric and unit:
- Battery Fleet:
battery-swapunits (e.g., "5 x swaps") - Electricity:
kWhunits (e.g., "2.5 x kWhs") - Network Access:
station-accessunits (e.g., "1 x access") - Transaction Count:
swap-transactionunits (e.g., "3 x transactions") - Infinity Quota:
BUSINESS_CONSTANTS.INFINITY_QUOTA = 100000000represents unlimited quota - Consumption Atomicity: Usage increments must be atomic - either complete successfully or not at all
- Quota modifications require proper validation and state persistence
1. Service Initialization Workflow¶
Purpose¶
Initialize services with appropriate quota levels based on service bundle configuration, business logic, and ServicePlanTemplate specifications.
Process Flow¶
ServicePlanTemplate → Template Validation → Service Configuration → Quota Calculation → ServiceState Initialization → ServiceAccount Persistence
Critical Requirements¶
- Template Integrity: ServicePlanTemplate must be validated before processing
- Business Rule Compliance: Quota calculation must follow configured business logic
- Atomic Initialization: All service states must be initialized atomically or not at all
- External Coordination: Downstream systems must be notified of initialization
- Rollback Capability: Failed initialization must support complete rollback
Implementation Requirements¶
- Read service bundle configuration from ServicePlanTemplate
- Apply business logic for quota calculation including infinity quota handling
- Initialize each service state with appropriate quota and default values
- Validate service dependencies and cross-service constraints
- Store initialized states in ServiceAccount
- Notify downstream systems of successful initialization
- Critical Sequence: Template validation MUST precede quota calculation
- Atomicity Requirement: Either all services initialize successfully or none do
- External Coordination: ARM, Odoo, and other systems must be informed of new service availability
2. Service Consumption Workflow¶
Purpose¶
Track service usage and increment 'used' counters according to service bundle logic during consumption events.
Process Flow¶
Consumption Request → Service Metric Validation → Pre-Consumption Validation → Availability Check → Usage Increment (by metric units) → Post-Consumption Validation → State Persistence → External Notifications → Signal if Needed
Service Consumption Event Method¶
Purpose: Record consumption events with specific amounts expressed in service metrics and communicate via MQTT
Consumption Event Structure:
{
"service_id": "svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard",
"consumption_amount": 5.0,
"consumption_unit": "battery-swap",
"consumption_event_id": "evt-swap-20250105-001",
"timestamp": "2025-01-05T14:30:00Z",
"context": {
"customer_id": "customer-001",
"station_id": "station-nairobi-001",
"transaction_type": "battery_swap"
}
}
MQTT Topic and Payload Conventions:
Service Consumption Topics:
- emit/abs/bss/service/{service_id}/consumed - Service consumption event
- echo/abs/bss/service/{service_id}/consumption_confirmed - Consumption acknowledgment
- emit/abs/bss/plan/{plan_id}/quota_updated - Quota status update
Consumption Event Payload:
{
"service_plan_id": "plan-001",
"service_id": "svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard",
"consumption_amount": 5.0,
"consumption_unit": "battery-swap",
"consumption_event_id": "evt-swap-20250105-001",
"quota_before": 100,
"quota_after": 95,
"used_before": 0,
"used_after": 5,
"quota_remaining": 95,
"quota_percentage_used": 5.0,
"timestamp": "2025-01-05T14:30:00Z",
"correlation_id": "consumption_plan-001_20250105_001",
"context": {
"customer_id": "customer-001",
"station_id": "station-nairobi-001",
"transaction_type": "battery_swap"
}
}
Consumption Amount Examples:
- Battery Fleet Service: 5.0 x battery-swap (5 swaps consumed)
- Electricity Service: 2.5 x kWh (2.5 kilowatt-hours consumed)
- Network Access: 1.0 x station-access (1 access event consumed)
- Transaction Count: 3.0 x swap-transaction (3 transactions counted)
Metric Validation Requirements:
- Consumption amount must be positive and match service's usage_unit
- Amount precision must align with service capabilities (e.g., integer swaps vs decimal kWh)
- Service-specific validation rules must be applied (e.g., "reasonable_consumption" for kWh)
- Cross-metric validation: Ensure consumption aligns with business logic (e.g., 1 swap = expected kWh range)
Critical Business Requirements¶
- Pre-Consumption Validation: Service availability, customer eligibility, and system readiness must be verified
- Bundle Dependency Logic: Bundle-specific consumption rules and cross-service dependencies must be applied
- Usage Atomicity: Usage increments must be atomic - either complete successfully or not at all
- Immediate Notification: External systems (Odoo, UXI) must be notified immediately upon consumption
- Audit Trail: Complete consumption history must be maintained for compliance
- Quota Threshold Monitoring: Approaching limits must trigger early warning systems
Implementation Requirements¶
- Metric-based Validation: Validate consumption amount matches service's
usage_unitand precision requirements - Pre-Validation: Service availability must be confirmed before allowing consumption
- Usage Tracking: Increment
usedcounter by exact consumption amount in service's metric units - Business Logic Enforcement: Apply service-specific validation rules (e.g., positive_count, reasonable_consumption)
- State Consistency: Service states must be updated consistently across all systems
- Rollback Capability: Failed consumption attempts must support complete rollback with
usedcounter restoration - External Integration: Billing and notification systems must be updated with consumption details in real-time
- Threshold Management: Quota warnings must be triggered at appropriate utilization levels
- Audit Compliance: All consumption events must be logged with metric amounts for compliance and analytics
- Atomicity Guarantee: Either all consumption updates succeed (increment
used, persist state, notify externals) or none do
3. Service Availability Workflow¶
Purpose¶
Determine service availability based on quota usage comparison, bundle logic, and real-time system status.
Availability Rules¶
- Individual Service: Available when
used < quotaand service status is active - Service Bundle: Available when ALL services in bundle are available (AND logic)
- Plan Level: Available when ALL bundles are available and plan is active
- Metric-based Assessment: Availability considers current
usedamount in service's metric units vsquotalimit - Real-time Calculation: Availability reflects most current
usedvalues after latest consumption events - System Dependencies: External system availability (ARM, payment systems) affects service availability
- Real-time Evaluation: Availability must be calculated on-demand with current system state
Process Flow¶
Availability Request → Individual Service Evaluation → Bundle Logic Application → Plan Level Assessment → External System Check → Return Availability Status
Critical Business Requirements¶
- Bundle AND Logic: ALL services in a bundle must be available for bundle availability
- External Dependencies: ARM asset availability and payment system status must be considered
- Performance Optimization: Frequent availability checks require intelligent caching strategies
- Real-time Updates: Availability changes must trigger immediate notifications to dependent systems
- Maintenance Windows: Scheduled maintenance must be factored into availability calculations
- Capacity Planning: Availability forecasting must support operational planning
Implementation Requirements¶
- Quota Assessment: Check each service's quota vs usage with current data
- Bundle Logic Enforcement: Apply bundle AND logic for comprehensive availability
- External Dependencies: Consider ARM asset availability and payment system status
- Comprehensive Status: Return detailed availability status with reasoning
- Performance Optimization: Implement intelligent caching where appropriate
- Change Notifications: Provide availability change notifications for dependent systems
- Edge Case Handling: Handle maintenance windows, system outages, and other exceptions
- Forecasting Support: Support availability forecasting for capacity planning
4. Quota Exhaustion Handling¶
4. Quota Exhaustion Handling¶
Exhaustion Detection Requirements¶
- Real-time Monitoring: Monitor quota usage during consumption with immediate detection
- Threshold Alerts: Detect when approaching limits (configurable warning thresholds)
- Immediate Response: Trigger exhaustion workflow immediately when
used >= quota - Early Warning System: Provide advance warnings at appropriate utilization levels
- Escalation Procedures: Handle both soft warnings and hard exhaustion scenarios
External System Coordination Requirements¶
- Odoo Integration: Notify for billing updates, quota top-up options, and customer communication
- UXI Notifications: Alert customer of quota status with self-service options
- Service Restrictions: Update service availability and implement appropriate restrictions
- ARM Coordination: Coordinate asset allocation restrictions based on quota status
- Analytics Updates: Update usage analytics and forecasting models
Resolution Pathway Requirements¶
- Quota Top-up: Enable quota increase through billing system integration
- Service Suspension: Implement graceful service suspension with customer communication
- Plan Modification: Support change to different service plan with higher quotas
- Emergency Override: Provide temporary quota extension for critical situations
- Service Termination: Enable graceful service shutdown with proper cleanup
5. Service Metric-based Consumption Tracking¶
Purpose¶
Provide a standardized method for recording consumption events with precise amounts expressed in underlying service metrics, ensuring accurate quota tracking and system-wide consistency.
Service Metrics Reference¶
Battery Fleet Services:
- svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard: usage_unit: "battery-swap"
- svc-battery-fleet-kenya-premium: usage_unit: "battery-swap"
- Consumption Examples: "5 x battery-swap", "1 x battery-swap"
- Validation: Positive integer values only
Energy Services:
- svc-electricity-refuel-kenya: usage_unit: "kWh"
- Consumption Examples: "2.5 x kWh", "0.8 x kWh", "5.2 x kWh"
- Validation: Positive decimal values, reasonable consumption ranges
Network and Transaction Services:
- svc-swap-network-kenya: usage_unit: "station-access"
- svc-swap-count-kenya: usage_unit: "swap-transaction"
- Consumption Examples: "1 x station-access", "3 x swap-transaction"
- Validation: Positive integer values, business logic constraints
Consumption Event Recording Method¶
Function Signature: recordServiceConsumption(serviceId, amount, unit, context)
Parameters:
- serviceId: Target service identifier (must exist in service registry)
- amount: Consumption quantity (must be positive, match service precision requirements)
- unit: Service metric unit (must match service's usage_unit)
- context: Additional consumption context (customer_id, station_id, transaction details)
Validation Sequence:
1. Service Existence: Verify service exists and is active
2. Metric Compatibility: Ensure unit matches service's usage_unit
3. Amount Precision: Validate amount precision matches service requirements
4. Business Rules: Apply service-specific validation rules
5. Availability Check: Confirm service available before consumption
6. Bundle Impact: Check if consumption affects bundle availability
Consumption Processing:
1. Pre-consumption State: Record current used value
2. Usage Increment: Add amount to service's used counter
3. Post-consumption Validation: Verify updated state consistency
4. External Notifications: Notify relevant systems with consumption details
5. Audit Recording: Log complete consumption event for compliance
Error Handling and Rollback¶
Validation Failures:
- Invalid service ID → Reject with SERVICE_NOT_FOUND
- Metric mismatch → Reject with INVALID_METRIC_UNIT
- Negative amount → Reject with INVALID_CONSUMPTION_AMOUNT
- Precision violation → Reject with INVALID_AMOUNT_PRECISION
Processing Failures:
- State persistence failure → Rollback used counter to pre-consumption value
- External notification failure → Retry with exponential backoff, maintain audit trail
- Bundle logic violation → Rollback entire consumption transaction
Recovery Requirements: - All consumption operations must be atomic - Failed operations must restore exact pre-consumption state - Audit trail must record both successful and failed consumption attempts - External systems must be notified of rollback events when applicable
6. Service-Specific Payment Events and Top-up Ledger¶
Purpose¶
Manage service-specific payment allocation and top-up transactions with separate ledger entries for each service, ensuring precise financial tracking and quota management.
Payment Event Structure¶
Service-Specific Payment Event: Since a ServicePlan contains multiple bundle services, each payment event must specify which service receives the payment allocation.
{
"payment_event_id": "pay-evt-20250105-001",
"service_plan_id": "plan-001",
"payment_type": "service_topup",
"payment_amount": 500.0,
"payment_currency": "KES",
"service_allocation": {
"target_service_id": "svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard",
"allocation_amount": 500.0,
"allocation_unit": "KES",
"quota_increment": 10.0,
"quota_unit": "battery-swap",
"unit_price": 50.0
},
"payment_method": "mobile_money",
"payment_reference": "MM-20250105-12345",
"timestamp": "2025-01-05T14:30:00Z",
"correlation_id": "payment_plan-001_20250105_001"
}
Top-up as Service Events¶
Top-up Service Event Structure: Top-ups are treated as special service events representing "I have topped up your service by this amount" and recorded as separate ledger entries.
{
"service_event_id": "srv-evt-topup-20250105-001",
"service_plan_id": "plan-001",
"event_type": "service_topup",
"target_service_id": "svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard",
"topup_details": {
"payment_amount": 500.0,
"payment_currency": "KES",
"unit_price": 50.0,
"quota_increment": 10.0,
"quota_unit": "battery-swap",
"quota_before": 5,
"quota_after": 15,
"calculation": "500.0 KES / 50.0 KES per swap = 10.0 swaps"
},
"payment_reference": "MM-20250105-12345",
"timestamp": "2025-01-05T14:30:00Z",
"correlation_id": "topup_plan-001_svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard_20250105_001"
}
MQTT Topics for Payment and Top-up Events¶
Payment Event Topics:
- emit/abs/bss/payment/{plan_id}/service_payment - Service-specific payment event
- echo/abs/bss/payment/{plan_id}/payment_confirmed - Payment confirmation
Top-up Service Event Topics:
- emit/abs/bss/service/{service_id}/topup_applied - Top-up service event
- echo/abs/bss/service/{service_id}/topup_confirmed - Top-up confirmation
- emit/abs/bss/plan/{plan_id}/quota_increased - Quota increase notification
Ledger Entry Requirements¶
Payment Ledger Entry:
{
"ledger_entry_id": "ledger-pay-20250105-001",
"entry_type": "payment",
"service_plan_id": "plan-001",
"target_service_id": "svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard",
"amount": 500.0,
"currency": "KES",
"direction": "credit",
"description": "Service top-up payment for battery fleet service",
"payment_reference": "MM-20250105-12345",
"timestamp": "2025-01-05T14:30:00Z"
}
Service Event Ledger Entry:
{
"ledger_entry_id": "ledger-srv-20250105-001",
"entry_type": "service_event",
"service_plan_id": "plan-001",
"target_service_id": "svc-battery-fleet-kenya-standard",
"quota_increment": 10.0,
"quota_unit": "battery-swap",
"direction": "credit",
"description": "I have topped up your service by 10.0 battery-swaps",
"related_payment_id": "pay-evt-20250105-001",
"timestamp": "2025-01-05T14:30:00Z"
}
Business Validation Requirements¶
Payment Event Validators (Validator Array Pattern): - Service ID must exist in service bundle - Payment amount must be positive - Service must support quota top-ups - Payment method must be valid and authorized - Unit price must match service configuration
Top-up Service Event Validators: - Target service must exist and be active - Quota increment calculation must be accurate - Related payment event must be confirmed - Service quota limits must be respected - Bundle logic must be maintained (AND logic)
Integration Requirements¶
External System Coordination: - Odoo Integration: Sync payment events with billing system - Payment Processors: Coordinate with mobile money and card processors - UXI Platform: Notify customers of successful top-ups - Analytics Platform: Track payment patterns and service usage
State Consistency Requirements: - Payment events must be atomic across payment and service accounts - Service events must update quota atomically - Failed payments must not affect service quotas - Ledger entries must maintain referential integrity
7. Service Integration and External System Coordination¶
Purpose¶
Coordinate service consumption workflows with external systems and maintain data consistency across all integrated platforms.
Integration Requirements¶
- Odoo Integration: Billing, customer management, and quota top-up operations coordination
- ARM Systems: Asset allocation, availability management, and fleet coordination
- UXI Platform: Customer notifications, self-service options, and real-time updates
- Analytics Platform: Usage tracking, forecasting, and performance analytics
- Monitoring Systems: Health monitoring, performance metrics, and alerting
Data Consistency Requirements¶
- Atomic Operations: State changes must be atomic across service boundaries
- Audit Trail: Complete audit trail of all service state changes must be maintained
- Conflict Resolution: Conflicts from concurrent updates must be resolved appropriately
- State Reconciliation: Periodic state reconciliation between systems must be supported
- Eventually Consistent: Temporary inconsistencies must be handled gracefully
8. Business Data Requirements¶
Core Data Structures¶
- ServiceState: Must track service_id, used (in service metric units), quota (in service metric units), availability, and consumption history
- ServiceBundle: Must track bundle_id, services collection, and bundle logic (currently AND)
- Service Dependencies: Must track cross-service dependencies and constraints
- Consumption Records: Must maintain audit trail of all service usage events with metric amounts and units
- Payment Events: Must track service-specific payment allocation with target_service_id and allocation details
- Service Events: Must track top-up events as separate ledger entries with quota increments
- Ledger Entries: Must maintain separate ledger for payment events and service events with referential integrity
- Service Metrics Mapping: Must maintain mapping of service_id to usage_metric and usage_unit for validation
- Availability Cache: May implement caching for performance optimization
Business Constants¶
- Infinity Quota: Use
BUSINESS_CONSTANTS.INFINITY_QUOTA = 100000000for unlimited service quotas - Warning Thresholds: Configure quota warning levels (suggested: 80%, 90%, 95%)
- Audit Retention: Define retention period for consumption audit records (suggested: 90 days)
- Cache TTL: Define cache time-to-live for availability queries (suggested: 5 minutes)
Key Business Functions Required¶
- Service Initialization: Initialize service states from ServicePlanTemplate with quota in appropriate metric units
- Consumption Event Recording: Record consumption events with specific amounts in service metric units (e.g., "5 x swaps", "2.5 x kWhs")
- Service-Specific Payment Processing: Process payments with target service allocation and quota calculation
- Top-up Service Event Recording: Record top-up events as separate service events with quota increments
- Ledger Management: Maintain separate ledger entries for payment events and service events
- Metric-based Usage Tracking: Update service usage counters with precise amounts in underlying service metrics
- Availability Assessment: Determine service/bundle availability in real-time based on quota vs used comparison
- Quota Management: Handle quota exhaustion detection and top-up scenarios with metric unit validation
- External Coordination: Coordinate with Odoo, ARM, UXI systems including consumption event details
- State Reconciliation: Maintain data consistency across systems with metric-accurate tracking
9. Workflow Validation and Quality Assurance¶
7. Workflow Validation and Quality Requirements¶
Business Validation Checkpoints¶
- Service Initialization: Services must be initialized with correct quotas from templates in appropriate metric units
- Template Integrity: ServicePlanTemplate must be validated before processing
- Consumption Accuracy: Usage must properly update counters with correct amounts in service metric units
- Metric Validation: All consumption events must specify amounts in underlying service metrics (e.g., "battery-swap", "kWh")
- Availability Correctness: Availability must accurately reflect quota status and system health with current used amounts
- Bundle Logic Enforcement: AND logic must be properly enforced across service bundles
- External System Coordination: Odoo, ARM, UXI systems must be notified of relevant changes with consumption details
- Data Persistence: ServiceAccount updates must be reliable and consistent with metric precision
- Quota Exhaustion Detection: Exhaustion and warnings must be detected promptly when used >= quota
- Error Recovery: Failed operations must support appropriate recovery mechanisms including used counter rollback
- Audit Compliance: Complete audit trail must be maintained for compliance requirements with metric amounts
Quality Assurance Requirements¶
- Service Exhaustion Response: System must respond appropriately to quota exhaustion
- Infinity Quota Support: Unlimited quotas must be handled correctly
- State Consistency: All quota tracking must be consistent across systems
- Performance Standards: System must meet response time requirements for availability checks
- Data Integrity: State management must maintain data integrity under all conditions
- Business Rule Compliance: All business rules must be enforced consistently
10. Performance and Monitoring Requirements¶
Performance Requirements¶
- Availability Checks: Must respond within acceptable time limits
- Consumption Updates: Must complete end-to-end processing efficiently
- Quota Calculations: Must complete calculations quickly for standard operations
- State Persistence: Must persist state changes with minimal latency
- Cache Performance: Must achieve high cache hit rates for availability queries
Monitoring Requirements¶
- Performance Metrics: Track response times, throughput, and error rates
- Health Monitoring: Monitor system component health and dependencies
- Usage Analytics: Track service consumption patterns and trends
- Quota Utilization: Monitor quota usage and exhaustion patterns
- Integration Status: Monitor external system connectivity and performance
11. Future Enhancements and Roadmap¶
11. Future Enhancement Opportunities¶
Planned Business Features (Phase 1 - Immediate)¶
- Dynamic Quota Adjustment: Real-time quota modifications based on usage patterns and business events
- Predictive Exhaustion Warnings: Advanced prediction of quota exhaustion with proactive customer outreach
- Enhanced Audit Capabilities: Comprehensive audit trails with compliance reporting and data retention policies
- Performance Optimization: Advanced caching strategies with intelligent invalidation
Planned Business Features (Phase 2 - Near-term)¶
- Automated Quota Top-up: Self-service and automated quota replenishment workflows
- Cross-Service Quota Sharing: Allow quota sharing between related services within bundles
- Real-time Usage Analytics: Live dashboards and analytics for usage patterns and optimization
- Advanced Error Recovery: Self-healing mechanisms and automated recovery procedures
Planned Business Features (Phase 3 - Long-term)¶
- AI-Powered Optimization: Machine learning optimization of quota allocation and service availability
- Multi-tenant Quota Management: Enterprise-level quota management across multiple customer segments
- Advanced Integration APIs: Enhanced APIs for third-party system integration and data exchange
- Blockchain Audit Trail: Immutable audit trail using blockchain technology for compliance
Integration Opportunities¶
- Customer Self-Service: Enhanced customer portal integration for quota management
- Business Intelligence: Advanced analytics and forecasting capabilities
- Automated Billing: Enhanced billing system integration with real-time synchronization
- Capacity Planning: Predictive analytics for strategic decision making and resource allocation
Summary¶
This BSS Service Consumption Workflow defines the business intent and requirements for service initialization, consumption tracking, availability management, and external system coordination. The workflow emphasizes:
Business Logic Focus¶
- Bundle AND Logic: All services in a bundle must be available for the bundle to be considered available
- No Partial Service Rule: Service must not proceed if any validation fails or conditions are not fully met
- Quota Management: Clear rules for quota tracking, exhaustion detection, and resolution pathways
- External Coordination: Requirements for coordinating with Odoo, ARM, UXI systems
Intent vs Implementation Separation¶
- Workflow Intent: Defines WHAT needs to happen and WHY (business requirements)
- Agent Implementation: Agent functions determine HOW to implement based on these requirements
- Pattern Selection: Implementation chooses appropriate MQTT patterns and timing based on intent
- Critical Sequences: Workflow specifies when order matters (e.g., validation before quota calculation)
Key Business Requirements¶
- Atomicity: Operations that must be all-or-nothing are clearly identified
- External Dependencies: Systems that must be coordinated are specified
- Data Consistency: Requirements for maintaining consistent state across systems
- Error Recovery: Business requirements for handling failures and recovery scenarios
- Audit Compliance: Business needs for tracking and compliance are defined
Implementation Note: This workflow provides the business logic foundation. Agent functions should interpret these requirements to select appropriate implementation patterns, timing, and messaging strategies based on the criticality and sequencing requirements specified in each workflow step.