ABS-Hub Ecosystem Architecture¶
Executive Summary¶
The ABS-Hub (Asset-Based Services Hub) represents a comprehensive digital ecosystem designed to enable and orchestrate asset-as-a-service business models. Built on a modern microservices architecture, the ABS-Hub connects physical assets, digital services, and human stakeholders through an intelligent, scalable platform that transforms traditional ownership models into flexible service delivery systems.
Vision Statement¶
Transforming Physical Assets into Digital Services
The ABS-Hub ecosystem enables businesses to transition from capital-intensive ownership models to flexible, service-based approaches. Whether it's battery swap networks, equipment rental, or shared mobility services, our platform provides the digital backbone that makes asset-as-a-service scalable, profitable, and sustainable.
Ecosystem Architecture Overview¶
The ABS-Hub ecosystem is designed as a five-tier architecture with clear separation of concerns, each layer building upon the capabilities of the layer below:
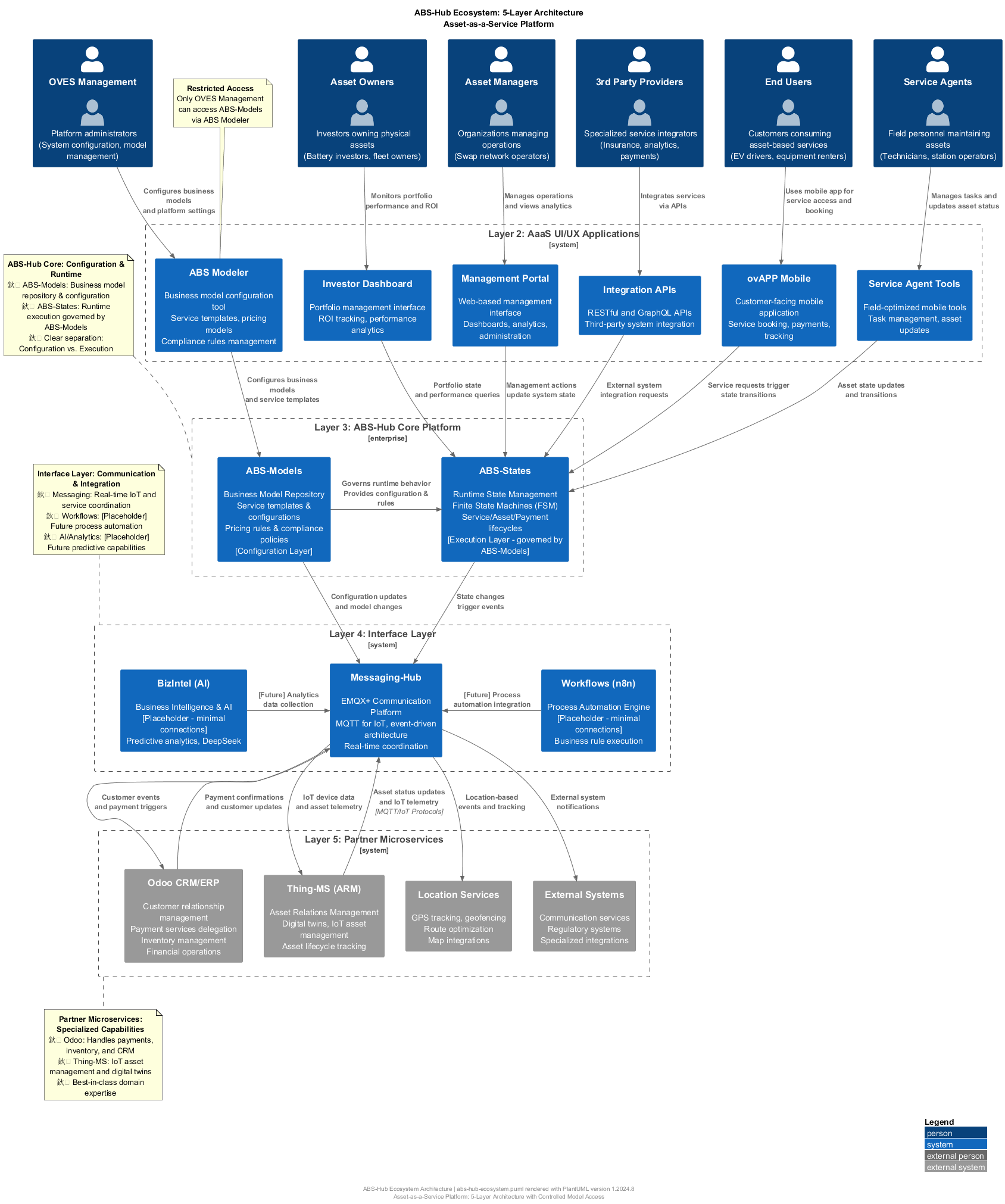
Figure 1: ABS-Hub Ecosystem 5-Layer Architecture - Complete system overview showing all stakeholders, applications, core platform components, interface layer, and partner microservices with their relationships and data flows.
Architecture Diagram: The diagram above provides a comprehensive overview of the ABS-Hub ecosystem architecture. The source PlantUML file is available at
diagrams/abs-hub-ecosystem.pumlfor interactive viewing and editing.
Tier 1: Application Users¶
The Human Ecosystem
Who They Are¶
The ABS-Hub ecosystem serves diverse stakeholders, each with unique needs and interactions:
End Users (Customers)¶
- Role: The individuals or businesses consuming asset-based services
- Examples: EV drivers using battery swap services, construction workers renting equipment, office workers using shared vehicles
- Value: Convenient access to assets without ownership burdens, pay-per-use pricing, maintained and reliable equipment
Service Agents (Field Personnel)¶
- Role: On-ground personnel who maintain, operate, and facilitate asset services
- Examples: Battery swap station attendants, equipment maintenance technicians, fleet coordinators
- Value: Mobile tools for real-time asset management, automated task assignment, performance tracking
Asset Owners (Investors)¶
- Role: Individuals or entities who own the physical assets and seek returns on investment
- Examples: Battery pack investors, equipment fleet owners, vehicle lessors
- Value: Portfolio visibility, revenue tracking, asset performance analytics, automated revenue distribution
Asset Managers (Operations)¶
- Role: Organizations responsible for day-to-day asset operations and optimization
- Examples: Battery swap network operators, equipment rental companies, mobility service providers
- Value: Operational dashboards, predictive maintenance, utilization optimization, customer service tools
Third-Party Service Providers¶
- Role: Specialized service providers integrating with the ecosystem
- Examples: Insurance providers, maintenance contractors, business intelligence services, payment processors
- Value: API access, data integration capabilities, revenue sharing models
What They Experience¶
- Seamless Service Access: Simple, app-based interactions for service consumption
- Real-Time Visibility: Live tracking of assets, services, and transactions
- Automated Operations: Reduced manual processes through intelligent automation
- Data-Driven Insights: Actionable analytics for optimization and growth
Tier 2: AaaS UI/UX Applications¶
Application-as-a-Service Interface Layer
This tier provides the digital touchpoints through which users interact with the ABS-Hub ecosystem. Each application is tailored to specific user types and use cases.
Customer-Facing Applications¶
Mobile Applications (ovAPP)¶
- Purpose: Primary interface for end-users to access asset services
- Capabilities:
- Service discovery and booking
- Real-time asset availability
- Payment processing and billing
- Service history and usage analytics
- Customer support integration
- Examples: Battery swap booking app, equipment rental platform, shared vehicle access
Web Portals¶
- Purpose: Comprehensive management interfaces for business users
- Capabilities:
- Dashboard-driven insights
- Multi-device responsive design
- Advanced reporting and analytics
- Administrative functions
- Examples: Fleet management portal, investor dashboard, operations command center
Operational Applications¶
Service Agent Mobile Tools¶
- Purpose: Field-optimized applications for service personnel
- Capabilities:
- Task assignment and tracking
- Asset status updates
- Maintenance logging
- Customer interaction tools
- Real-time communication with operations center
Management Dashboards¶
- Purpose: Strategic oversight and operational control interfaces
- Capabilities:
- KPI monitoring and alerting
- Resource allocation optimization
- Predictive analytics
- Financial performance tracking
- Compliance and audit trails
Integration APIs¶
- Purpose: Programmatic access for third-party integrations
- Capabilities:
- RESTful and GraphQL APIs
- Real-time event streaming
- Webhook integrations
- Rate limiting and security controls
- Comprehensive documentation
Tier 3: ABS-Hub Core¶
The Intelligent Orchestration Engine
The ABS-Hub Core represents the heart of the ecosystem—a sophisticated platform that orchestrates all interactions, manages business logic, and ensures seamless coordination between assets, services, and stakeholders.
Core Components¶
ABS-Models (Business Logic Engine)¶
- Purpose: Defines and enforces business rules and service models
- Access Control: Only accessible through the ABS Modeler application in Tier 2, restricted to OVES Management
- Capabilities:
- Service Plan Templates: Reusable business model definitions for different markets and use cases
- Pricing Models: Dynamic pricing engines supporting multiple revenue models (subscription, pay-per-use, hybrid)
- Contract Management: Automated contract creation, modification, and enforcement
- Compliance Engine: Ensures adherence to local regulations and business rules
- Business Value: Enables rapid market expansion with localized business models while maintaining operational consistency
ABS-States (State Management System)¶
- Purpose: Runtime state management layer governed by ABS-Models using advanced Finite State Machines (FSMs)
- Governance: Operates under the rules and templates defined in ABS-Models
- Capabilities:
- Service Lifecycle Management: Tracks customer service states from signup to completion
- Asset State Tracking: Monitors physical asset conditions, availability, and utilization
- Payment State Management: Handles complex payment flows and subscription lifecycles (delegated to Odoo)
- Event-Driven Transitions: Automatic state changes based on real-world events with O(1) performance
- Business Value: Ensures consistent service delivery and enables predictive operations with mathematical precision
Core Business Logic Engine¶
- Purpose: Orchestrates business processes and coordinates with ABS-Models and ABS-States
- Capabilities:
- Agent System: Data-driven agents for reactive business logic execution
- FSM Engine: Optimized finite state machine implementation with O(1) performance
- Template Management: Reusable workflow templates and versioning
- Event Processing: Real-time event handling and business rule execution
- Business Value: Provides the core intelligence that transforms business models into executable processes
Cross-Cutting Capabilities¶
Security & Compliance¶
- End-to-end encryption and secure communication
- Role-based access control and audit trails
- Regulatory compliance automation
- Data privacy and protection frameworks
Scalability & Performance¶
- Cloud-native architecture supporting global deployment
- Auto-scaling based on demand patterns
- High-availability design with 99.9% uptime SLA
- Performance monitoring and optimization
Developer Experience¶
- Comprehensive APIs and SDKs
- Real-time debugging and monitoring tools
- Extensive documentation and examples
- Sandbox environments for testing
Tier 4: Interface Layer¶
Communication and Integration Orchestration
The Interface Layer serves as the communication orchestrator between the ABS-Hub Core and external systems, providing a clean separation of concerns and future-proofing the architecture for new integrations.
Messaging-Hub (Primary Communication Orchestrator)¶
- Purpose: Centralized communication hub managing all external system interactions
- Capabilities:
- Protocol Translation: Converts between different messaging protocols (MQTT, HTTP, WebSocket)
- Message Routing: Intelligent routing of messages between internal and external systems
- Event Orchestration: Coordinates complex event flows across multiple systems
- Connection Management: Maintains reliable connections to partner microservices
- Integration Benefits: Provides a single point of control for all external communications while maintaining loose coupling
Future Integration Placeholders¶
Workflows (n8n) - [Placeholder]¶
- Purpose: Visual workflow automation for complex business processes
- Current Status: Marked as placeholder with minimal connections
- Future Capabilities: Process automation, external system integration, business rule execution
BizIntel (AI) - [Placeholder]¶
- Purpose: AI-powered business intelligence and predictive analytics
- Current Status: Marked as placeholder with minimal connections
- Future Capabilities: Predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, revenue optimization
Design Principles¶
- Simplified Connections: Clean separation between core business logic and external integrations
- Messaging-Hub Driven: All external communications flow through the centralized messaging hub
- Future-Ready: Architecture designed to accommodate new integrations without core system changes
- Minimal Coupling: Placeholder components maintain minimal connections until fully implemented
Tier 5: Partner Microservices¶
Specialized System Integrations
The foundation tier consists of specialized microservices that provide domain-specific capabilities, allowing the ABS-Hub to leverage best-in-class solutions while maintaining architectural flexibility.
Odoo CRM/ERP Platform¶
- Purpose: Comprehensive customer relationship and enterprise resource management
- Payment Services: All payment processing is delegated to Odoo for consolidated financial operations
- Capabilities:
- Customer Lifecycle Management: Complete customer journey tracking from lead to service completion
- Financial Operations: Invoicing, accounting, financial reporting, and all payment processing
- Inventory Management: Asset tracking, procurement, and supply chain coordination
- Partner Management: Vendor, supplier, and service provider relationship management
- Integration Benefits: Leverages mature, proven business management capabilities without reinventing core enterprise functions
Thing-MS (Asset Relations Management)¶
- Purpose: Specialized IoT asset management and digital twin services
- Capabilities:
- Digital Twin Creation: Virtual representations of physical assets with real-time synchronization
- Asset Lifecycle Tracking: Complete asset history from manufacturing to decommissioning
- Maintenance Orchestration: Predictive and scheduled maintenance coordination
- Performance Analytics: Asset utilization, efficiency, and performance monitoring
- Integration Benefits: Provides deep IoT expertise and asset management capabilities specifically designed for connected devices
External System Integrations¶
Authentication and Security Services¶
- SSO/Cloak authentication integration
- Multi-factor authentication
- Role-based access control
- Security audit and compliance
Location Services¶
- GPS tracking and geofencing
- Route optimization
- Geographic analytics
- Map integrations
Communication Services¶
- SMS and email notifications
- Push notification services
- Multi-language support
- Communication analytics
Analytics and AI Services¶
- Machine learning model deployment
- Big data processing
- Business intelligence tools
- Custom analytics engines
Business Benefits¶
For Service Providers¶
- Rapid Market Entry: Deploy new asset-based services in weeks, not months
- Operational Efficiency: Automated processes reduce operational overhead by up to 60%
- Scalable Growth: Platform scales from pilot projects to enterprise deployments
- Revenue Optimization: AI-driven insights increase revenue per asset by 25-40%
For Asset Owners¶
- Maximized Returns: Optimized utilization increases asset ROI
- Reduced Risk: Diversified revenue streams and insurance integrations
- Market Expansion: Access to new markets and customer segments
- Passive Income: Automated operations reduce management overhead
For End Users¶
- Cost Savings: Pay-per-use models reduce total cost of ownership by 30-50%
- Convenience: On-demand access to assets when and where needed
- Quality Assurance: Professionally maintained and regularly updated assets
- Flexibility: Scale usage up or down based on actual needs
Use Case Examples¶
Battery Swap Networks¶
- Scenario: Electric vehicle drivers need quick battery replacement services
- ABS-Hub Role: Orchestrates station availability, pricing, maintenance, and user experience
- Value Creation: Enables sustainable EV adoption through convenient charging alternatives
Construction Equipment Sharing¶
- Scenario: Construction companies need temporary access to specialized equipment
- ABS-Hub Role: Manages equipment availability, booking, maintenance, and logistics
- Value Creation: Reduces capital requirements while ensuring equipment availability
Shared Mobility Services¶
- Scenario: Urban residents need occasional vehicle access without ownership
- ABS-Hub Role: Coordinates vehicle allocation, user management, and operational optimization
- Value Creation: Provides sustainable urban mobility solutions
Technology Advantages¶
Modern Architecture¶
- Cloud-Native Design: Built for scalability, reliability, and global deployment
- Microservices Architecture: Modular, maintainable, and technology-agnostic
- API-First Approach: Enables easy integration and customization
- Event-Driven Systems: Real-time responsiveness and loose coupling
Industry Standards¶
- GraphQL APIs: Modern, efficient data querying and manipulation
- MQTT Messaging: Industry-standard IoT communication protocols
- TypeScript Development: Type-safe, maintainable code development
- Container Deployment: Kubernetes-ready for enterprise environments
Open Integration¶
- Vendor Agnostic: Not locked into any specific technology vendor
- Standards Compliant: Follows industry best practices and standards
- Extensible Design: Easy to add new capabilities and integrations
- Future-Proof: Architecture designed to evolve with technology advances
Implementation Approach¶
Phase 1: Foundation (3-6 months)¶
- Core ABS-Hub platform deployment
- Basic service model implementation
- Initial user interfaces
- Pilot deployment with limited scope
Phase 2: Integration (6-9 months)¶
- Full microservice integration
- Advanced workflow automation
- Comprehensive analytics implementation
- Extended pilot operations
Phase 3: Scale (9-12 months)¶
- Multi-market deployment
- Advanced AI capabilities
- Third-party ecosystem development
- Full production operations
Phase 4: Optimization (Ongoing)¶
- Continuous improvement based on data insights
- New feature development
- Market expansion
- Ecosystem growth
Conclusion¶
The ABS-Hub ecosystem represents a paradigm shift in how we think about asset utilization and service delivery. By combining cutting-edge technology with proven business models, we enable organizations to transform their assets into sustainable, scalable service offerings.
The five-tier architecture ensures that each stakeholder—from end users to asset owners—receives maximum value while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions. The platform's modular design and open integration capabilities future-proof investments while enabling rapid innovation.
Whether you're an established enterprise looking to transition to service-based models or a startup building the next generation of asset-sharing services, the ABS-Hub ecosystem provides the foundation for sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the digital economy.
For more information about implementing the ABS-Hub ecosystem for your organization, please contact our solutions team.